close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media









You may ask, is silicon a metal? The answer is no. Silicon is a metalloid. Metalloids have traits of metals and nonmetals. Silicon is special in the periodic table. It has a shiny look but it breaks easily. Silicon makes up about 27.7% of the Earth's crust:
Element | Approximate % by weight |
|---|---|
Silicon | 27.7 |
There are eight elements that are metalloids:
Element | Symbol |
|---|---|
Boron | B |
Silicon | Si |
Germanium | Ge |
Arsenic | As |
Antimony | Sb |
Tellurium | Te |
Polonium | Po |
Astatine | At |
Silicon is a metalloid. It is not a metal. It has some traits of metals. It also has traits of nonmetals. Silicon looks shiny. But it is brittle. It breaks if you bend it. Metals can bend, but silicon cannot. Silicon is a semiconductor. It can carry electricity. But it does not do this as well as metals. Metalloids like silicon are important for technology. People use them in electronics. They are also used in solar panels. Silicon has special properties. These make it needed for modern devices. It helps devices work well.
If you wonder if silicon is a metal, you should check its traits and spot on the periodic table. Silicon is in group 14. It sits between metals and nonmetals. This spot gives it mixed traits. Silicon looks shiny like metal. But it snaps if you bend it. Silicon does not carry electricity as well as metals. It works as a semiconductor. That means it can carry electricity sometimes. Silicon has covalent bonds, just like nonmetals. These things make scientists call silicon a metalloid, not a metal.
Look at this table to see how silicon compares with metals and nonmetals:
Characteristic | Metalloids (like silicon) | Metals | Nonmetals |
|---|---|---|---|
Appearance | Metallic-looking, brittle | Shiny, ductile | Dull or shiny |
Electrical Conductivity | Moderate, semiconductors | Good conductors | Poor conductors |
Thermal Conductivity | Moderate | Good | Poor |
Oxides | Weakly acidic/amphoteric | Basic | Acidic |
You can see that asking if silicon is a metal is not easy. The answer depends on its mixed traits.
Metalloids are elements with both metal and nonmetal traits. You find them in a zigzag line on the periodic table. If you ask if silicon is a metal, you learn it is a key metalloid. Metalloids often work as semiconductors. They come in different forms. They carry heat and electricity, but not as well as metals. The word metalloid means it is not fully a metal or a nonmetal.
Here are some facts about metalloids:
Metalloids include boron, silicon, and arsenic.
They look shiny but break easily.
Metalloids can make covalent compounds.
They are important in electronics and industry.
Silicon is used in silicon steel. This steel is needed for transformers and electric motors. Adding silicon to steel makes it resist electricity more. It also helps magnetic properties. This makes energy move better. Is silicon a metal? No, but being a metalloid makes it very important for technology today.
Metals look shiny and feel smooth. Most metals bend without snapping. You can make wires or sheets from them. Metals let electricity flow very well. Copper and iron are metals used in wires and tools. Metals also move heat fast. They have high conductivity, so electricity passes through them easily.
Property | Metals |
|---|---|
Appearance | Shiny, metallic |
Brittleness | Not brittle |
Conductivity | Very high |
Flexibility | Ductile |
Nonmetals are different from metals. They look dull and feel rough. Nonmetals snap if you try to bend them. They do not let electricity flow well. Sulfur and carbon are nonmetals you see often. Nonmetals have low conductivity. They do not move heat fast. Most nonmetals make covalent bonds.
Property | Nonmetals |
|---|---|
Appearance | Dull |
Brittleness | Brittle |
Conductivity | Very low |
Flexibility | Not ductile |
Silicon is special among metalloids. It has a blue-gray shine. Silicon looks shiny like metals. But it breaks if you bend it. This is like nonmetals. Silicon makes covalent bonds, just like nonmetals do. But silicon is also a semiconductor. It carries electricity better than nonmetals. But it does not carry it as well as metals. Look at the table below to compare:
Property | Metal | Nonmetal | Silicon |
|---|---|---|---|
Appearance | Shiny | Dull | Metallic gray |
Brittleness | No | Yes | Yes |
Conductivity (S/m) | 10^6 - 10^7 | < 1000 | 1000 |
Metalloids like silicon have conductivity of 1000 S/m.
Metals have conductivity from 10^6 to 10^7 S/m.
Nonmetals have conductivity less than 1000 S/m.
Silicon is not just a metal or a nonmetal. It shines like a metal but breaks like a nonmetal. Its conductivity is in the middle. Silicon is used in electronics. It can let electricity flow or stop it. This mix of traits is why silicon is called a metalloid.
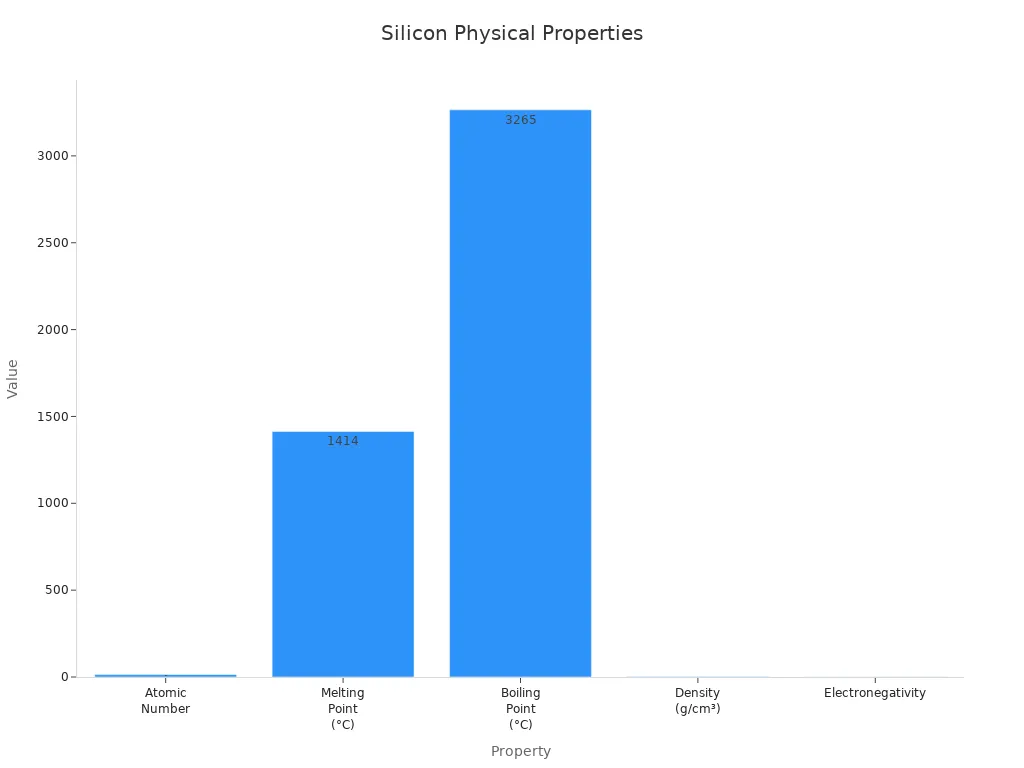
When you look at a metalloid, it shines. The surface has a bluish-grey shine. This shine looks like iron or silver. The color is brighter than most nonmetals. At room temperature, it is a solid. This is like many metals. Silicon’s atomic number is 14. It is in group 14, called the carbon family.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Appearance | Bluish-grey metallic lustre |
Phase at STP | Solid |
Atomic Number | 14 |
Group | 14 (Carbon family) |
A metalloid does not carry electricity like metals. It is a semiconductor. This means it lets electricity move, but not as well as copper or gold. People use it in electronics for this reason. It can switch between letting electricity pass and stopping it. Its conductivity is in the middle. This makes it different from metals and nonmetals.
Property | Silicon | General Characteristics of Metalloids |
|---|---|---|
Electrical Conductivity | Electrical semiconductors | |
Bonding Type | Covalent | Both metals and nonmetals |
Structural Similarity | Nonmetals | Similar to nonmetals |
The Mohs scale shows how hard it is. Silicon has a value of 7. This is harder than most nonmetals. Some metals are harder, but many are softer. If you try to bend it, it breaks. Tests use a Vickers diamond indenter to check cracks. These tests use different forces to see how brittle it is. Simulations help show how cracks grow and how tough it is.
Mohs hardness is 7, so it is pretty hard.
It is harder than many nonmetals.
Some metals are harder, but many are not.
Tests use a Vickers diamond indenter.
Forces like 300 mN, 500 mN, 750 mN, and 1000 mN are used.
Cracks show how brittle it is.
Simulations help study how tough and brittle it is.
The shine, medium conductivity, and hardness make a metalloid special. These things show why it is not a metal, even if it shares some traits with metals.
Silicon is found in Group 14. Its atomic number is 14. This group is between metals and nonmetals. Silicon is special because it has traits from both sides. The table below shows silicon’s place:
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Symbol | Si |
Atomic Number | 14 |
Group | 14 |
Silicon’s spot helps show why it acts as a bridge. It conducts electricity better than nonmetals. But it does not conduct as well as metals. Silicon looks shiny but feels brittle. These things show it has mixed traits.
There are other elements called metalloids. They sit on a zigzag line between metals and nonmetals. Here are some common metalloids and their atomic numbers:
Boron (B, Atomic Number 5)
Silicon (Si, Atomic Number 14)
Germanium (Ge, Atomic Number 32)
Arsenic (As, Atomic Number 33)
Antimony (Sb, Atomic Number 51)
Tellurium (Te, Atomic Number 52)
Polonium (Po, Atomic Number 84)
Astatine (At, Atomic Number 85)
Metalloids have special features that make them useful. They can have different oxidation states. This means they join in many chemical reactions. They carry heat better than nonmetals. But they do not carry heat as well as metals. Their ionization energies and electronegativities are in the middle. Most metalloids, like boron and arsenic, melt at higher temperatures than nonmetals. These traits make metalloids helpful in many ways.
Metalloids are important in science and industry. Silicon is used in computer chips and solar panels. It helps control electricity. Boron makes materials stronger and lighter. This helps build airplanes. Antimony makes alloys stronger and helps them resist heat. These alloys are used in car batteries. Metalloids help connect metals and nonmetals. They give us materials with special traits for new technology.
You have learned that silicon is a metalloid, not a metal. Silicon looks shiny like a metal. But it breaks if you try to bend it. It also works as a semiconductor. Metals are used to make things like bridges and wires. Nonmetals are used in medicine and to clean water. Metalloids, such as silicon, are important for electronics and computers.
Field | Silicon’s Impact |
|---|---|
Semiconductors | Runs computers, smartphones, and satellites |
Solar Energy | Makes solar cells work better |
Medical Devices | Helps make devices safer and work well |
Silicon’s unique features help change science and technology today. You can find silicon in digital devices and solar panels everywhere.
Silicon looks shiny like a metal. But it breaks instead of bending. You cannot stretch it. Silicon is a semiconductor. It carries electricity better than nonmetals. But metals carry electricity even better.
Pure silicon is safe to touch. It does not hurt your skin. You see silicon in many things at home. Do not breathe in silicon dust. It can hurt your lungs.
Silicon and germanium are in the same group. Both are semiconductors. Silicon is easier to find. It costs less money. Germanium works better in cold electronics.
Silicon is used in chips and solar panels. It is a semiconductor. You can control electricity with it. Silicon helps devices work faster. It also helps them use less energy.